Petrochemicals
Urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO(NH₂)₂. It is a colorless, odorless substance that is relatively non-toxic and highly soluble in water. Over 90% of global urea production is used as nitrogen-containing chemical fertilizers. In soil, urea undergoes hydrolysis to form ammonia and carbon dioxide. The ammonia produced in this process is further oxidized to nitrate by soil bacteria, making it available for plant uptake. Urea is also a crucial raw material in the chemical industry, used in the production of various plastics, especially formaldehyde-urea resins, adhesives like urea-formaldehyde and urea-melamine formaldehyde, potassium cyanate, and urea nitrate.

Chemical analysis
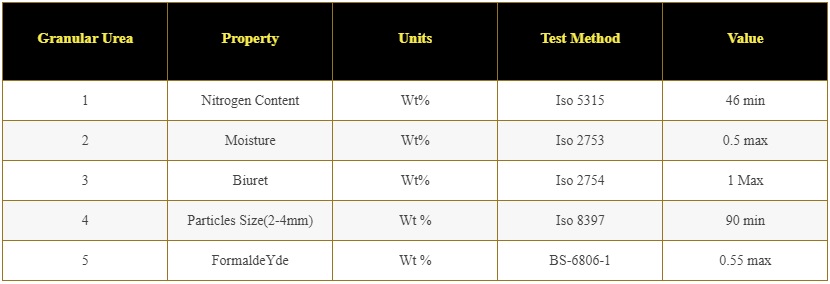
Granular Urea
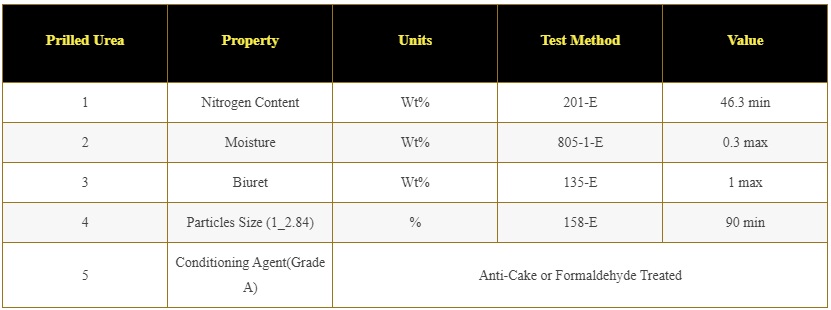
Prilled Urea
Bitumen
As a trusted global partner, Radan Prime Trading specializes in sourcing and brokering high-quality bitumen for various applications. Our extensive network allows us to negotiate competitive prices and ensure timely delivery to your preferred port. Here’s what we offer:
Quality Assurance:
- We prioritize bitumen derived from vacuum bottoms—the base material used in bitumen production.
- Rigorous quality control ensures that our offerings meet or exceed industry standards.
Bitumen Grades:
- Penetration Grades: Ideal for road paving, our range includes 30/40, 60/70, and 80/100.
- 60/70: Widely used for road projects across various temperatures.
- 80/100: Excellent for paving roads in India and Central African countries.
- Viscosity Grades (VG):
- VG 10: Suitable for cold regions due to better temperature resistance.
- VG 30: Offers superior quality and performance compared to 60/70.
Contact us to discuss your bitumen needs, and let us be your reliable partner in the global bitumen market
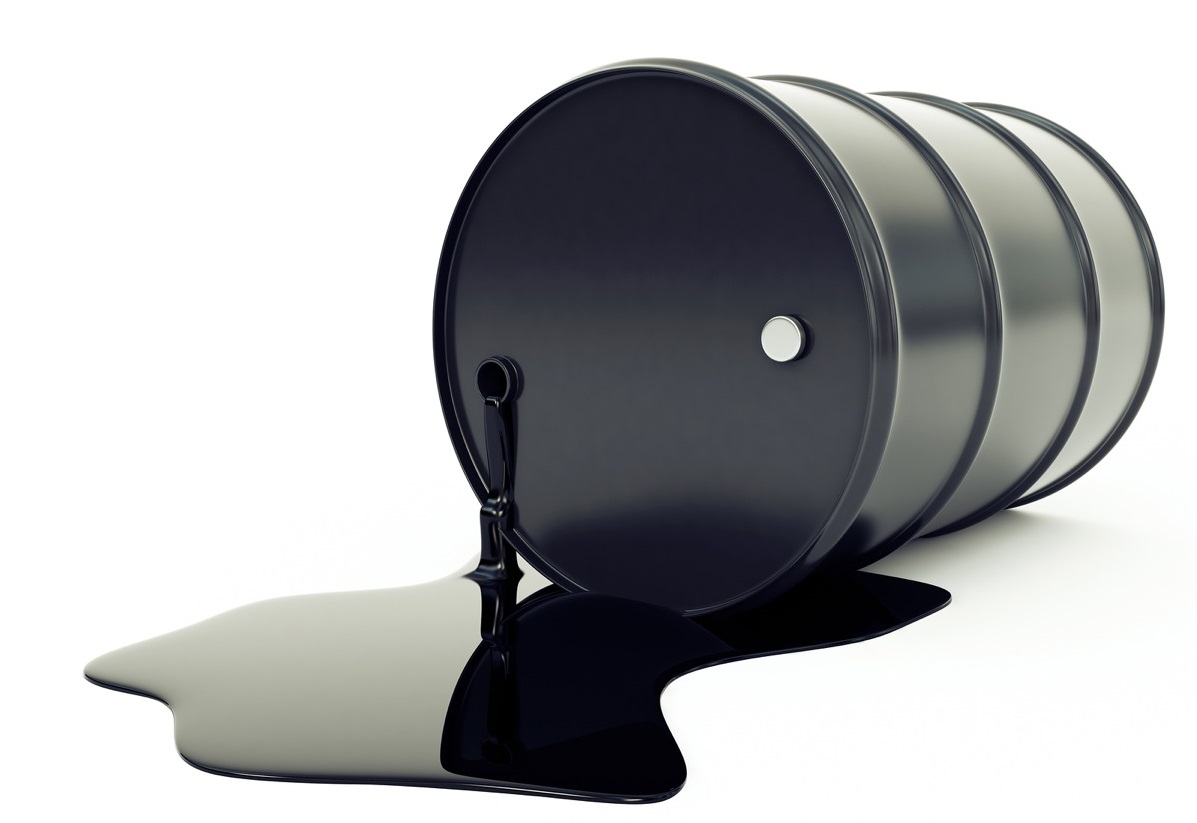

Chemical analysis
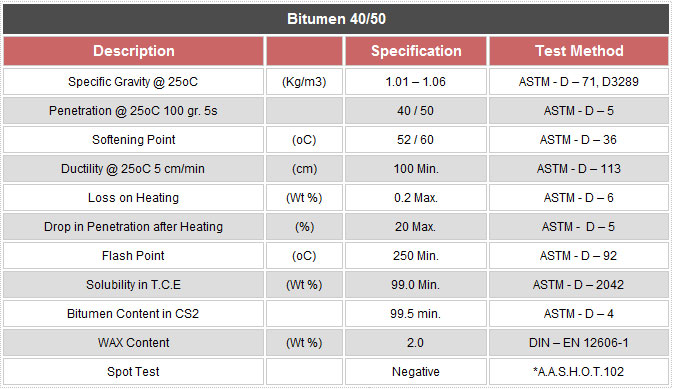
Bitumen 40/50
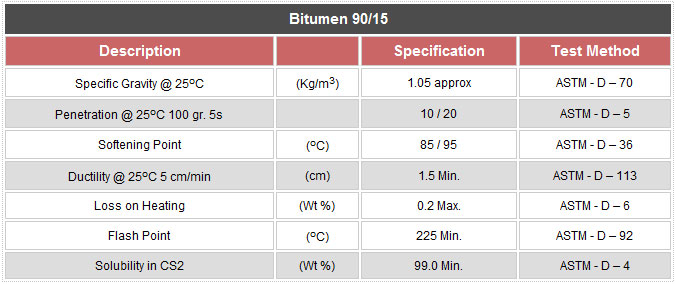
Bitumen 60/70
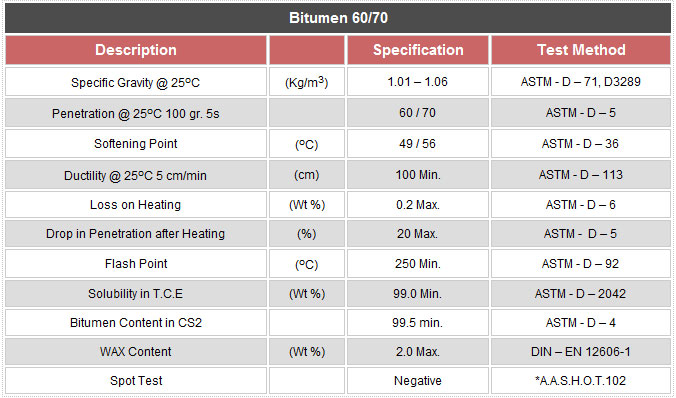
Bitumen 85/25
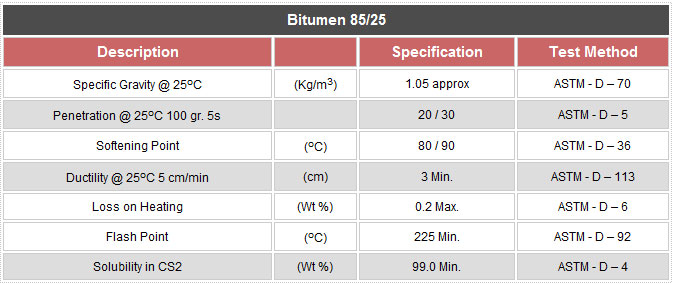
Bitumen 85/100
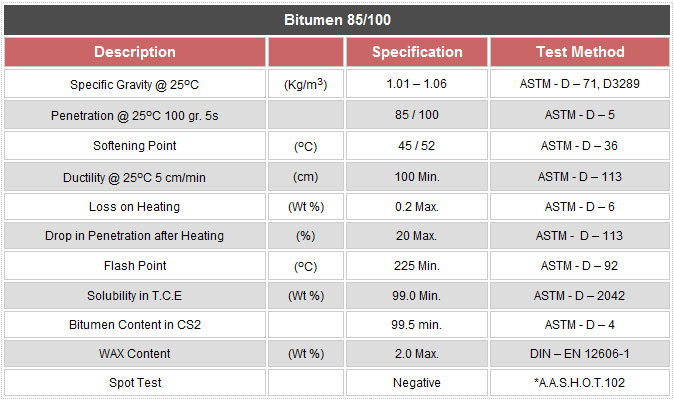
Bitumen 90/15
virgin base oil
we specialize in brokering high-quality virgin base oils sourced directly from reputable refineries. These base oils serve as the foundation for a wide range of lubricants, industrial fluids, and specialty products. Here’s what you need to know:
- Virgin base oils are unblended, pure hydrocarbon oils obtained through refining crude oil.
- They exhibit excellent thermal stability, viscosity, and oxidation resistance.
- Group I: These base oils have low viscosity index (VI) and are suitable for less demanding applications.
- Group II: With improved VI and better performance, Group II base oils find use in automotive and industrial lubricants.
- Group III: High VI and excellent stability make Group III base oils ideal for synthetic lubricants.
- Group IV (PAO): Polyalphaolefins (PAOs) are fully synthetic base oils with exceptional properties.
- Group V: Includes specialty oils (esters, silicones, etc.) for specific applications.

Chemical analysis
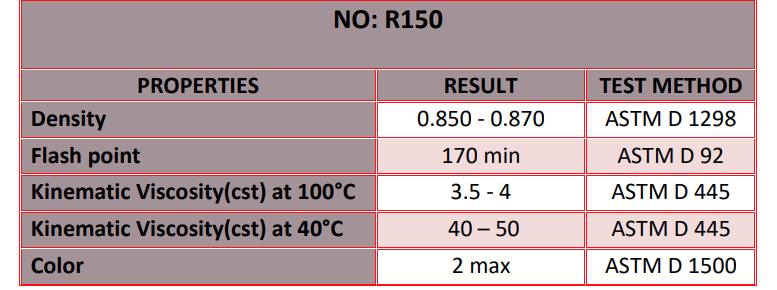
R150
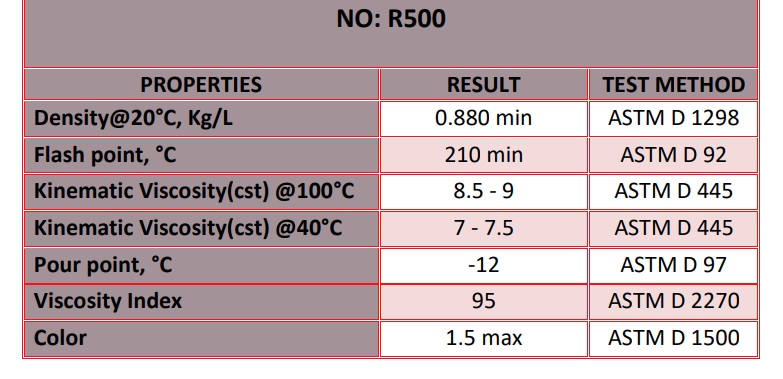
R500
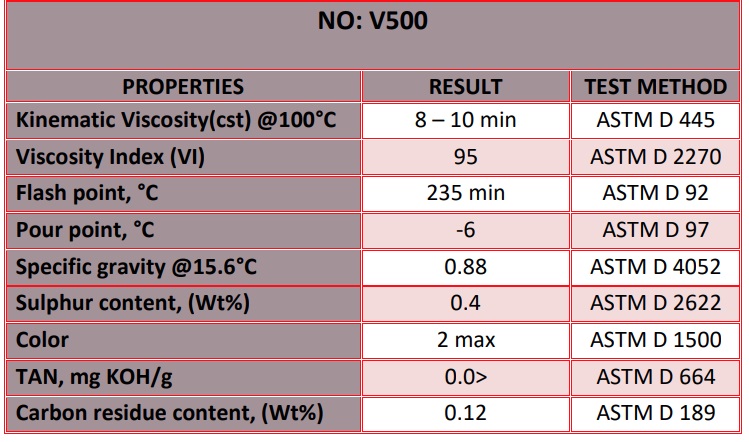
v500
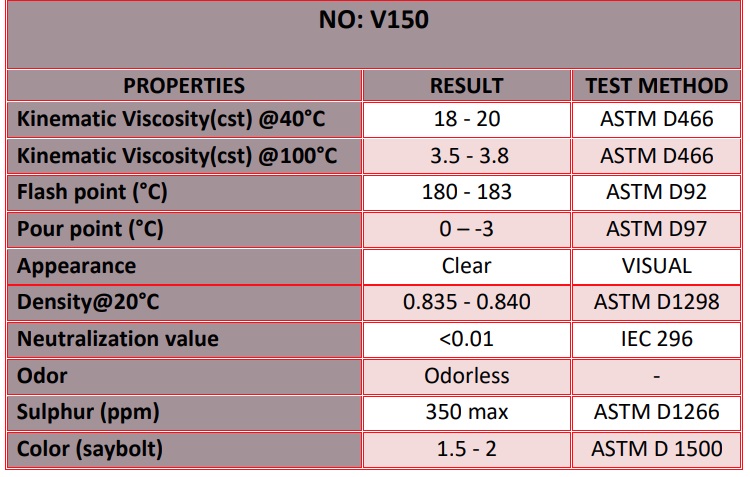
V150